Add SonarCloud/SonarQube to Episerver/Optimizely 12 project using Github actions
by Stanisław Szołkowski
In my previous post Add Github pipelines/workflows to Episerver 12 project I have briefly explained how to add simple pipeline/workflow to Episerver/Optimizely 12 project. Having project build for each PR and on main branch push is nice improvement, but we can make it even better. For this example I will add SonarCloud integration to my existing workflow from my previous post. You can see it on my Foundation fork - it will be using Github actions on each pull request and on main branch.
What is SonarQube/SonarCloud?
I personally think that SonarQube best describe itself in following quote:
SonarQube is an open source platform to perform automatic reviews with static analysis of code to detect bugs, code smells and security vulnerabilities on 25+ programming languages SonarQube
SonarCloud is cloud based SonarQube working as SaaS solution, so we don’t have to host SonarQube server on premise. It is almost the same in terms of features and the way how it works, so it can be used basically interchangeably with SonarQube except the way how it is hosted.
In my own word it is universal tool for static code analysis that can be used for most popular programming languages, so it can be easily adapted by different sets of projects and be used as company standard tool. It is also relatively easy to use and configure.
What kind of value does it bring?
SonarQube helps to catch a lot of problems with the code by pointing out our code smells and vulnerabilities that might cause big headache later. It will also help to maintain code quality by promoting good code practices or even enforcing them by failing the builds that doesn’t met selected quality gate criterial.
Its great feature is integration with pull requests for most popular source control providers like github, azure dev ops, bitbucket or gitlab which gives early feedback what needs to be improved in new code that was committed.
Official SonarQube list of features
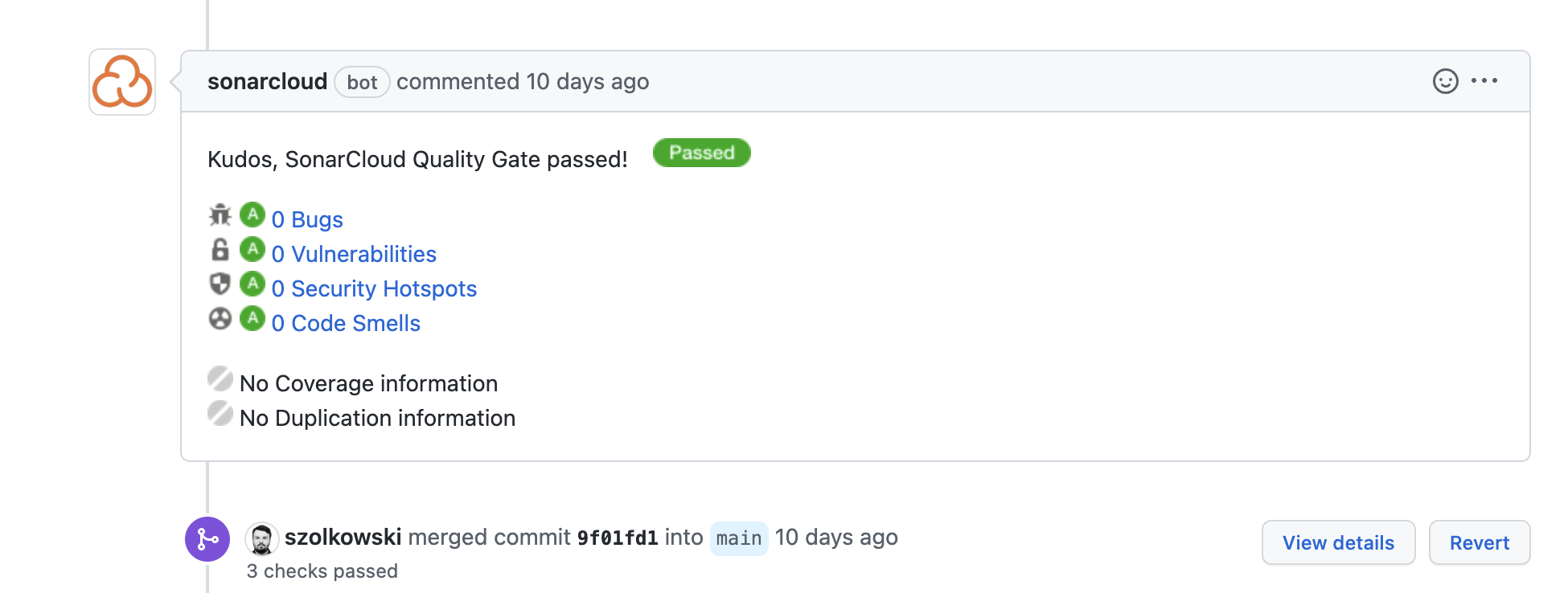
Full workflow/pipeline snippet and steps to make it work
Here is code snipped for my workflow enhanced byt SonarCloud integration. To understand what it does you might want to take a look into this post with all steps explained: Add Github pipelines/workflows to Episerver 12 project
- Register on sonarcloud.io
- Create organization and bind it with your Github account following instruction
- Create project in SonarCloud
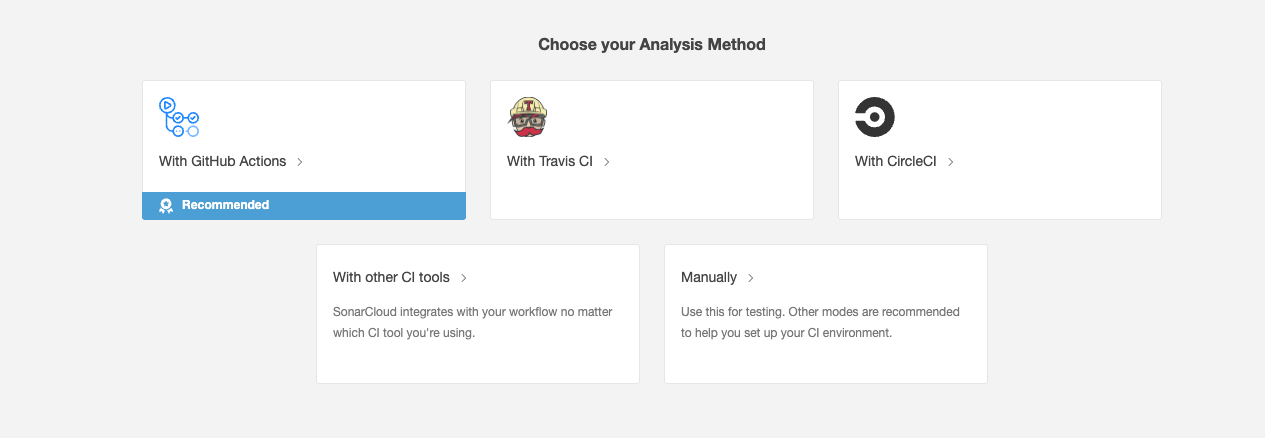
- Choose analysis method “with github actions”
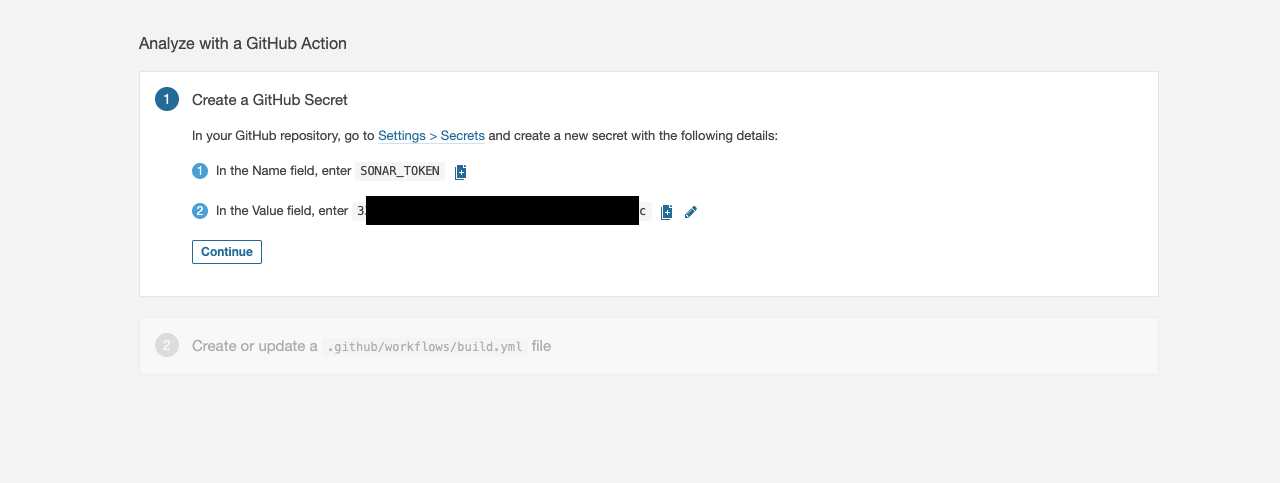
- Setup secret in your repository
- Create or edit file:
.github/workflows/ci-episerver.yml(file name is up to you) and copy below code. Remember to replaceYOUR_PROJECT_KEYandYOUR_ORGANIZATIONwith keys from Sonarcloud page.
name: Episerver CI Build
on:
push:
branches:
- main
pull_request:
branches: [ '**' ]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Set up JDK 11
uses: actions/setup-java@v2
with:
distribution: 'adopt'
java-version: '11'
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- name: Setup .NET
uses: actions/setup-dotnet@v1
with:
dotnet-version: 6.0.x
- name: Setup Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v2
with:
node-version: '14.18.2'
- name: Setup Episerver/Optimizely nuget feed
shell: pwsh
run: dotnet nuget add source https://nuget.optimizely.com/feed/packages.svc -n Optimizely
- name: Cache SonarCloud packages
uses: actions/cache@v1
with:
path: ~/sonar/cache
key: $-sonar
restore-keys: $-sonar
- name: Cache SonarCloud scanner
id: cache-sonar-scanner
uses: actions/cache@v1
with:
path: ./.sonar/scanner
key: $-sonar-scanner
restore-keys: $-sonar-scanner
- name: Install SonarCloud scanner
if: steps.cache-sonar-scanner.outputs.cache-hit != 'true'
shell: pwsh
run: |
New-Item -Path ./.sonar/scanner -ItemType Directory
dotnet tool update dotnet-sonarscanner --tool-path ./.sonar/scanner
- name: Restore dependencies
run: dotnet restore
- name: Sonar Begin
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: $
SONAR_TOKEN: $
shell: pwsh
run: |
./.sonar/scanner/dotnet-sonarscanner begin /k:"<YOUR_PROJECT_KEY>" /o:"<YOUR_ORGANIZATION>" /d:sonar.login="$" /d:sonar.host.url="https://sonarcloud.io"
- name: Dotnet build
shell: pwsh
run: dotnet build --no-restore --configuration Release
- name: NPM install
shell: pwsh
working-directory: ./src/Foundation
run: npm ci
- name: NPM build
shell: pwsh
working-directory: ./src/Foundation
run: npm run dev
- name: Sonar End
if: always()
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: $
SONAR_TOKEN: $
shell: pwsh
run: |
./.sonar/scanner/dotnet-sonarscanner end /d:sonar.login="$"
The only thing left is to Git commit & Git push!
How does it works?
SonarScanner requires JAVA 11 to run, so following lines will set up java for our pipeline:
- name: Set up JDK 11
uses: actions/setup-java@v2
with:
distribution: 'adopt'
java-version: '11'
We can often skip SonarScanner fetching packages by adding cache on them.
- name: Cache SonarCloud packages
uses: actions/cache@v1
with:
path: ~/sonar/cache
key: $-sonar
restore-keys: $-sonar
Caching SonarScanner itself will cut build time by even more time.
- name: Cache SonarCloud scanner
id: cache-sonar-scanner
uses: actions/cache@v1
with:
path: ./.sonar/scanner
key: $-sonar-scanner
restore-keys: $-sonar-scanner
This step will install SonarScanner used for collecting data that will be send to SonarQube/SonarCloud. This will try to use cache from above steps in order to save some time.
- name: Install SonarCloud scanner
if: steps.cache-sonar-scanner.outputs.cache-hit != 'true'
shell: pwsh
run: |
New-Item -Path ./.sonar/scanner -ItemType Directory
dotnet tool update dotnet-sonarscanner --tool-path ./.sonar/scanner
For project containing .NET we need to start SonarScanner before project will be build. Token values will be loaded from repository secrets.
- name: Sonar Begin
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: $
SONAR_TOKEN: $
shell: pwsh
run: |
./.sonar/scanner/dotnet-sonarscanner begin /k:"<YOUR_PROJECT_KEY>" /o:"<YOUR_ORGANIZATION>" /d:sonar.login="$" /d:sonar.host.url="https://sonarcloud.io"
After build step we add SonarScanner end steps which will collect and pre-processed all data for our build and send it to SonarCloud/SonarScanner
- name: Sonar End
if: always()
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: $
SONAR_TOKEN: $
shell: pwsh
run: |
./.sonar/scanner/dotnet-sonarscanner end /d:sonar.login="$"
Further improvements
Right now we have set up SonarCloud integration with minimal configuration required, but as every mature tool it can be configured to better meets our specific needs. I will explore this in next posts!